1.Power System
Diesel Engines – Supply mechanical or electrical power.
Generators – Convert mechanical energy into electrical power.
Electrical Control System – Distributes power to various rig components.
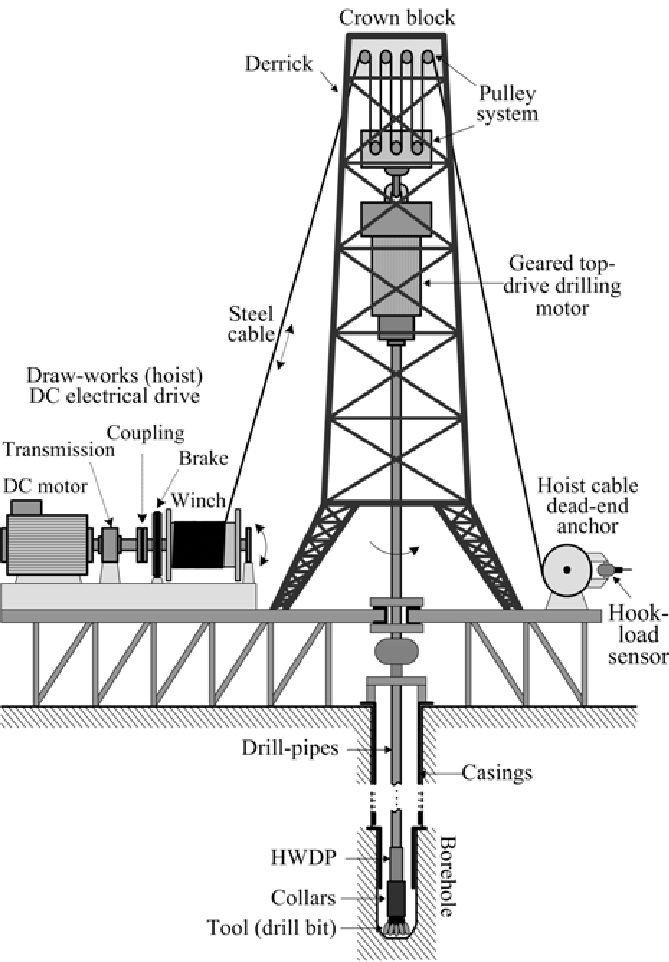
2.Hoisting System
Derrick or Mast – A tall steel structure that supports the drilling equipment.
Crown Block – A set of pulleys mounted at the top of the derrick.
Traveling Block – Moves up and down, supporting the drill string.
Draw Works – A system of winches and cables that control the movement of the drill string.
Drilling Line – A strong steel cable used to raise and lower the traveling block.
3.Rotary System
The rotary system enables the drill bit to rotate and penetrate the subsurface rock formations. It consists of:
Rotary Table – A rotating platform that turns the drill string.
Top Drive (Alternative to Rotary Table) – A motorized system that provides torque directly to the drill string.
Kelly (Older Rigs) – A square or hexagonal pipe that transmits rotary motion.
Drill Pipe – Hollow steel pipes that transmit drilling fluid and torque to the drill bit.
Drill Bit – A cutting tool designed to break through rock formations.
4.Circulating System
Main components include:
Mud Pumps – High-pressure pumps that circulate drilling fluid (mud) down the drill string.
Mud Pits – Storage tanks for drilling fluid.
Shale Shaker – A vibrating screen that removes solid cuttings from the drilling fluid.
Desander and Desilter – Remove finer solids from the drilling mud.
Mud Gas Separator – Separates gas from the drilling fluid.
5.Blowout Prevention System (BOP)
The BOP system is a critical safety feature that prevents uncontrolled well blowouts. It includes:
Annular BOP – A flexible, rubber-sealed device that can close around the drill pipe.
Ram-Type BOP – Uses steel rams to seal the wellbore completely.
Accumulator Unit – A hydraulic system that provides pressure to operate the BOPs.
6.Well Control System
Choke Manifold – Controls the pressure during a kick (unexpected formation fluid entry).
Kill Line – Allows the circulation of heavy drilling fluid to control well pressure.
Mud Logger Unit – Monitors gases and cuttings to detect signs of hydrocarbon presence.
7.Pipe Handling System
Catwalk & Pipe Racks – Storage for drill pipes and casing.
Iron Roughneck – An automated tool for making and breaking drill pipe connections.
Tongs & Slips – Manual or hydraulic tools for handling drill pipes.
8.Monitoring & Control System
Driller’s Console – Central control unit for the drilling operation.
Downhole Sensors – Measure pressure, temperature, and drilling efficiency.
Logging While Drilling (LWD) & Measurement While Drilling (MWD) – Real-time data acquisition tools.
