What is Stuck Pipe?
Stuck pipe occurs when the drill pipe, drill string, or casing becomes immovable in the wellbore. This can prevent further progress in drilling, and if unresolved, it may require costly interventions or even abandonment of the well.
Types of Stuck Pipe
1. Differential Sticking
Cause: Occurs when part of the drill string is pressed against the wellbore wall due to a pressure differential between the drilling mud and the formation.
Indicators: Inability to rotate or pull the drill string, with no movement detected.
Solution: Reducing the overbalance pressure or spotting lubricating agents to free the pipe.
2. Mechanical Sticking
Cause: Results from physical obstructions such as wellbore instability, cavings, or key seats trapping the drill string.
Indicators: Resistance to pulling or rotating with increased torque.
Solution: Employing jarring tools or reaming operations to remove obstructions.
Causes of Stuck Pipe
1. Hole Instability
Formation collapse or swelling shale may narrow the wellbore, trapping the pipe.
2. Key Seating
Occurs when the drill string cuts into the formation, creating a narrow groove where the pipe gets stuck.
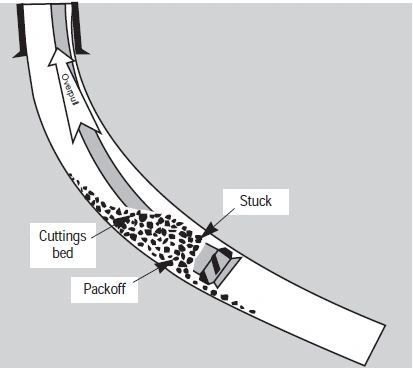
3. Improper Hole Cleaning
Accumulated cuttings in the annulus can pack around the drill string, restricting movement.
4. Differential Pressure
High overbalance pressure can press the drill string against permeable formations.
5. Equipment and Operational Issues
Poorly designed bottom-hole assemblies (BHAs) or inadequate drilling practices can contribute to stuck pipe incidents.
Prevention Methods
1. Optimized Drilling Practices
Maintain proper weight on the bit, rotation speed, and mud flow rate.
2. Efficient Hole Cleaning
Ensure adequate mud circulation to remove cuttings from the wellbore.
3. Proper Well Design
Minimize sharp doglegs and key seat potential by ensuring smooth well paths.
4. Monitor Drilling Parameters
Use real-time data to identify signs of impending stuck pipe, such as sudden torque changes or drag.
5. Use of Preventive Tools
Employ stabilizers, reamers, and lubricants to reduce sticking risks.
Solutions for Stuck Pipe
1. Freeing Techniques
Back-Off Operation: Unscrewing the pipe at a preselected point to recover the free section.
Fishing Tools: Use overshots or spears to recover stuck sections.
2. Chemical Spotting
Spotting fluids, including lubricants or acids, can dissolve or reduce the binding forces holding the pipe.
3. Mechanical Interventions
Jar tools or downhole hammers can deliver impact forces to dislodge the stuck pipe.
4. Sidetracking
In cases where the pipe cannot be freed, sidetracking around the stuck section may be necessary.
